A new hurricane season forecast issued by The Weather
Channel on Tuesday says we can expect the number of named storms and hurricanes
in the 2015 Atlantic season to stay below historical averages.
Numbers of Atlantic Basin named storms, those that attain at
least tropical storm strength, hurricanes, and hurricanes of Category 3
intensity forecast by The Weather Channel (right column) and Colorado State
University (center column) compared to the 30-year average (left column).
A total of nine named storms, five hurricanes and one major
hurricane are expected this season, according to the forecast prepared by The
Weather Channel Professional Division. This is below the 30-year average of 12
named storms, six hurricanes and three major hurricanes. A major hurricane is
one that is Category 3 or stronger on the Saffir-Simpson Hurricane Wind Scale.
Meteorologist Dr. Todd Crawford of The Weather Channel
Professional Division says, “Both the dynamical models and our proprietary
statistical models suggest a relatively quiet tropical season this year."
The Weather Channel forecast for below-average activity
during the 2015 Atlantic hurricane season is consistent with what Colorado
State University (CSU) said in its forecast issued on April 9. CSU's forecast
called for seven named storms, including three hurricanes, one of which is
predicted to attain major hurricane status.
The CSU outlook, headed by Dr. Phil Klotzbach in
consultation with long-time hurricane expert Dr. William Gray, is based on a
combination of 29 years of statistical predictors, combined with analog seasons
exhibiting similar features of sea-level pressure and sea-surface temperatures
in the Atlantic and eastern Pacific Oceans.
 |
2014 Atlantic Hurricane Season Tracks |
Here are four questions about this outlook and what it means
for you.
2014 Atlantic Hurricane Season Tracks
Tracks of all Atlantic tropical cyclones attaining at least
tropical storm strength in the 2014 hurricane season.
Q: Does this mean a less destructive season?
There is no strong correlation between the number of storms
or hurricanes and U.S. landfalls in any given season.
"It is important to note that our - The Weather Channel
- forecasts are for the total number of storms that may occur anywhere within
the Atlantic Ocean, and do not attempt to predict the number of storms that
will make landfall in the U.S.," said Dr. Peter Neilley, vice president of
Global Forecasting Services at WSI.
The 2014 season featured the fewest number of named storms
in 17 years (eight storms), but also featured the strongest landfalling hurricane
in the mainland U.S. in six years (Hurricane Arthur on the Outer Banks), and
featured two back-to-back hurricane hits on the tiny archipelago of Bermuda
(Fay, then Gonzalo).
Furthermore, six of those eight storms became hurricanes,
and Gonzalo was the strongest Atlantic hurricane since Igor in 2010.
(RECAP: 2014 Hurricane Season)
In 1983, there were only four named storms, but one of them
was Alicia, a Category 3 hurricane which clobbered the Houston-Galveston area.
The 2010 season featured 12 hurricanes and 19 named storms,
which tied 1995 for the third most named storms in any Atlantic season, at the
time. But not a single hurricane, and only one tropical storm, made landfall in
the U.S during that active season.
In other words, a season can deliver many storms, but have
little impact, or deliver few storms and have one or more hitting the U.S.
coast with major impact.
Therefore, it's important to be prepared for hurricanes and
tropical storms every year, regardless of seasonal forecasts.
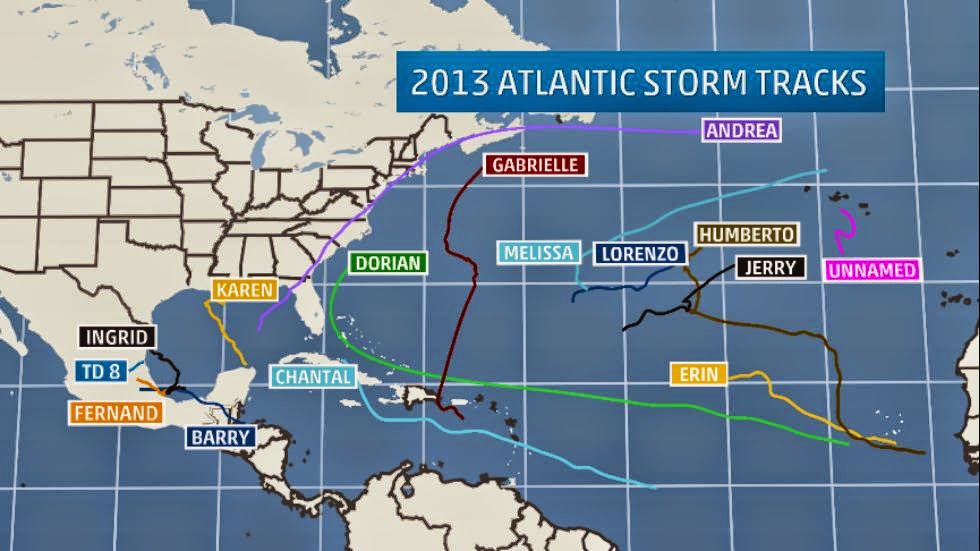 |
| 2013 Atlantic hurricane season storm tracks. |
Potential impact of El Nino on 2015 Atlantic hurricane
season.
Q: Will El Niño play a role?
El Nino was first officially declared by NOAA as winter
wound down. As of this early April forecast, El Niño, a periodic warming of the
equatorial Pacific waters, has been given a 60 percent chance of persisting
into the fall, according to NOAA's Climate Prediction Center.
Dr. Crawford says, "A new El Niño event is emerging
that will likely be stronger than last year’s weaker event. The cooler ocean
temperatures and subsidence/shear associated with the El Niño event will likely
be a deterrent for widespread tropical cyclone development in the
Atlantic."
There is a body of scientific evidence linking the
occurrence of El Niño with increased wind shear in the tropical Atlantic Basin,
which is one factor, along with dry air, that limits the development and
strengthening of tropical cyclones.
However, exactly where the warming of the equatorial Pacific
waters takes place and the magnitude of that warming plays at least a partial
role in the number of Atlantic named storms.
- Warming in the eastern equatorial Pacific: lower number of
Atlantic tropical cyclones
- Warming in the central equatorial Pacific: higher number
of Atlantic tropical cyclones
Klotzbach and Gray of CSU found five other hurricane seasons
with comparable Atlantic and Pacific sea-surface temperatures both in February-March,
as well as what is forecast for August-October: 1957, 1987, 1991, 1993 and
2014. Those years averaged eight named storms, four hurricanes, and 1-2 major
hurricanes.
Despite the low numbers in those years, in addition to
2014's Hurricane Arthur, there were two other historic hurricanes during those
seasons:
- Hurricane Bob (1991): One of the costliest and most
intense New England hurricanes on record ($1.5 billion damage; 17 killed; 5-8
foot storm surge in Rhode Island; waves battered south coasts of Nantucket and
Martha's Vineyard)
- Hurricane Audrey (1957): Only Category 4 June Atlantic
hurricane on record; Seventh deadliest Atlantic hurricane with at least 416
killed.
In short, the exact role El Niño may play in the 2015 season
remains uncertain.
(MORE: El Niño Facts Behind the Impacts)
Sea-surface temperature anomalies in the Atlantic Basin in
late March 2015 compared to 1980-2010 average. Blue/purple colors denote cooler
than average SSTs. Yellow/orange/red colors denote warmer than average
SSTs. (Klotzbach and Gray April 2015
hurricane season forecast)
Q: Any other factors in play?
"Aggregate Atlantic basin sea surface temperatures are
as cool as they’ve been since 2009, and are at the second coolest levels in 20
years," said Dr. Crawford.
Looking at the Atlantic Basin as a whole as of late March
2015, warmer sea-surface temperatures (hereafter, SSTs) were in place in the
western Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Sea but generally cooler-than-average SSTs
dominated in the eastern Atlantic Ocean from the western African coast to about
halfway to the Windward Islands.
All other factors – such as the amount of wind shear and dry
air aloft – being equal, warmer waters offer more heat to fuel the tropical
cyclone.
It is important to note, however, that a large majority of
the destructive hurricanes during the record-setting 2005 hurricane season
developed in the western Atlantic Basin.
"The big question marks with this season's predictions
are how strong El Niño is going to be, as well as if tropical and North
Atlantic sea-surface temperature anomalies remain as cool as they are
now," said Klotzbach and Gray.
2013 Atlantic hurricane season storm tracks.
Q: Why were the last two seasons relatively quiet?
We mentioned the somewhat paradoxical 2014 Atlantic
hurricane season earlier. Fewest named storms since 1997, but back-to-back
strikes on Bermuda, as well as Hurricane Arthur ruining the July 4th holiday on
the Outer Banks of North Carolina.
In 2014, Klotzbach and Gray noted July sea-surface
temperatures in the main development region between the Lesser Antilles and
Africa were the coolest since July 2002. Interestingly, sea-surface
temperatures were actually warmer than average in a broad swath of the western
Atlantic Ocean, western Caribbean Sea, and Gulf of Mexico.
Vertical wind shear, namely the change in wind direction
and/or speed with height, was found to be near the strongest on record in July
2014 over the Caribbean Sea, according to the CSU study. Wind shear disrupts
tropical cyclones or inhibits them from developing by displacing thunderstorms
from the center of circulation.
Following Arthur, five remaining named storms forming in the
Atlantic Ocean all took north, then northeast turns away from the U.S.
mainland, thanks to the orientation of winds aloft and the orientation of the
Bermuda high. Tropical Storms Dolly and Hanna buried themselves in eastern
Mexico and Central America, respectively.
In the 2013 season, for the first time since 1994, no
hurricanes stronger than Category 2 developed. Since the satellite era began in
1960, only four other seasons failed to produce a single Category 3 or stronger
hurricane (1994, 1986, 1972, 1968).
"By most measures, 2013 was one of the strangest years
in the tropical Atlantic in many decades," said Dr. Crawford.
"The 'usual suspects' of pre-season indicators
suggested a reasonably active season as relative warm Atlantic SSTs and an
expected lack of El Niño resulted in fairly bullish seasonal forecasts."
While the number of storms predicted (14) in 2013 was above
the long-term average, the dominance of dry air and wind shear limited the
intensity of existing storms or squelched the development of others.





No comments:
Post a Comment